The NSX Edge can be configured to provide site-to-site VPN connectivity using IPsec. If you’;re not familiar with IPsec, I suggest having a read up on that first. As IPsec is a standard, information already published will be transferable.
An NSX Edge can connect to any other device that supports IPsec. If a peer is not an NSX Edge, you need to verify that it will be compatible. The NSX Edge supports the following.
- Phase 1 mode: Main Mode
- Phase 2 mode: Quick Mode
- Diffie-Helman Group 2 and 3
- Digital cert and PSK
- Static routing only
- Encryption: AES, AES-256, AES-GCM and 3DES
While on the topic of support, each NSX Edge supports 10 remote sites and up to 6000 VPN tunnels. The number of tunnels you can actually use depends on the size of the NSX edge.
- Compact: 512
- Large: 1600
- Quad Large: 4096
- Xtra Large: 6000
The number of tunnels needed is local subnets x peer subnets. If Site A peer has 3 subnets and site B peer has 10, then 30 tunnels are used.
If one or both of the NSX Edges are behind NAT, then the peer IP address used will be the public IP address, the NAT will perform the translation for the traffic to get to the other peer Edge.
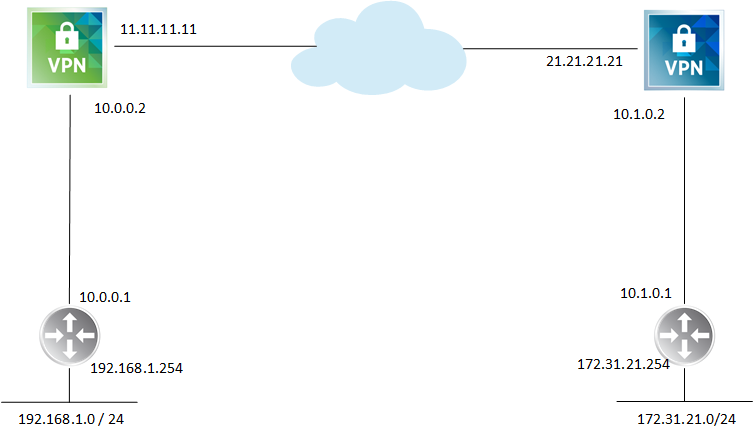
For an example of configuring an inter-site IPsec VPN I have done a mock configuration using VMwares HOL based on the topology below. The left network is Site A and the right is Site B
The link between the DLR and the ESG is called a transit network and uplink LIFs are used.
For this example, I will assume that the interfaces have already been configured for the ESG and DLR.
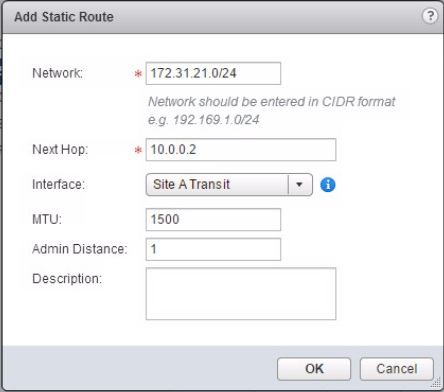
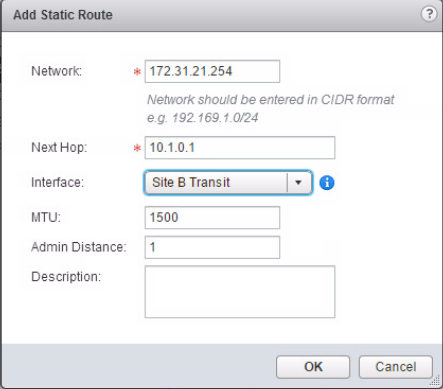
On the DLR we need to configure a static route to get to 172.31.21.0/24 using the ESG. This could also be configured as the default route.
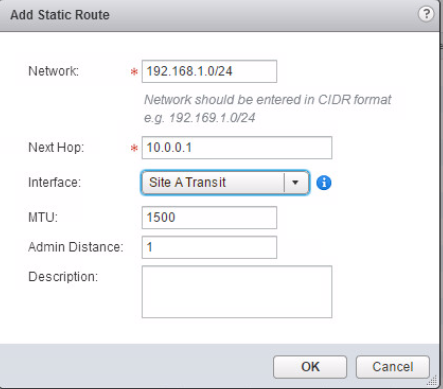
We now need to configure a route on the ESG so it knows how to send traffic to the 192.168.1.0/24 network.
We repeat the steps at Site B
DLR
ESG
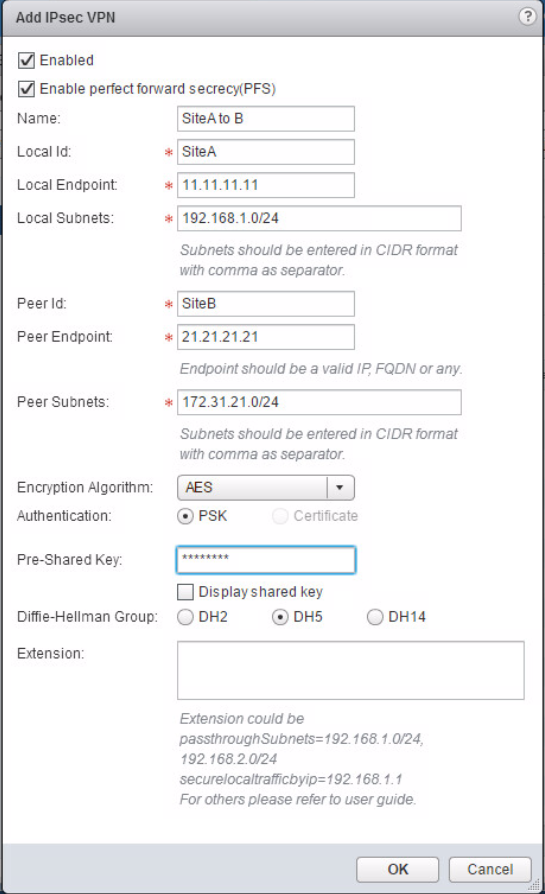
Now it’;s just a matter of configuring the IPSec VPN connections on both ESG’;s
- If using a PSK, the Locale ID can be anything you like, if using digital certificates then it must match the common name on the cert.
- Local end point is the Uplink LIF IP
- Peer ID is the ID of the peer that the ESG connects to. Just like Locale ID, it can be anything if using PSK but must match common name if used digital cert.
- Peer endpoint is the IP address of the peer.
- Peer subnets are the subnets that can be reached at the peer. The ESG will add static routes for these subnets on completion.
- Configure Algorithm and Authentication. These must be the same at both sites.
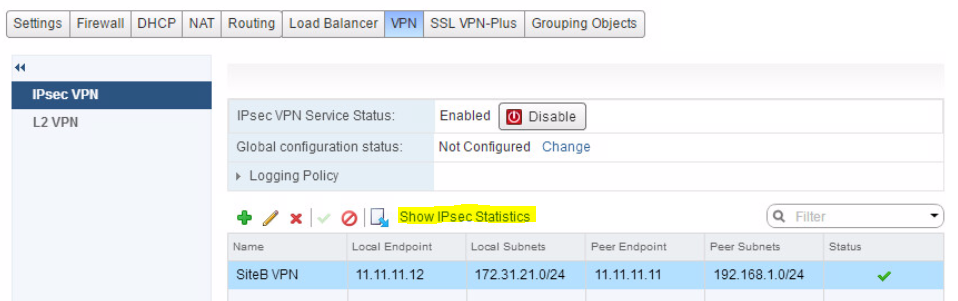
Firewall rules are automatically created for the VPN at each site.
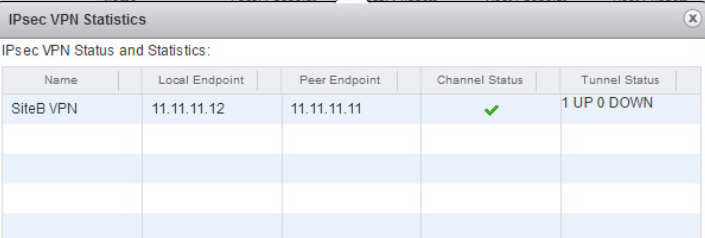
IPsec tunnel status can be confirmed by clicking “Show IPsec Statistics”
If you notice that the local IP is not 21.21.21.21 for Site B, instead it’;s 11.11.11.12. That was changes in order to get the two ESGs to connect in the HOL with putting more configuration into this.